By 2040 there could be 288 million cases of AMD
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of vision loss especially among older adults. Characterised by the deterioration of the central retina (the macula), AMD can lead to irreversible central vision loss in late stages, particularly in those of us aged over 60.
Global Prevalence and Burden
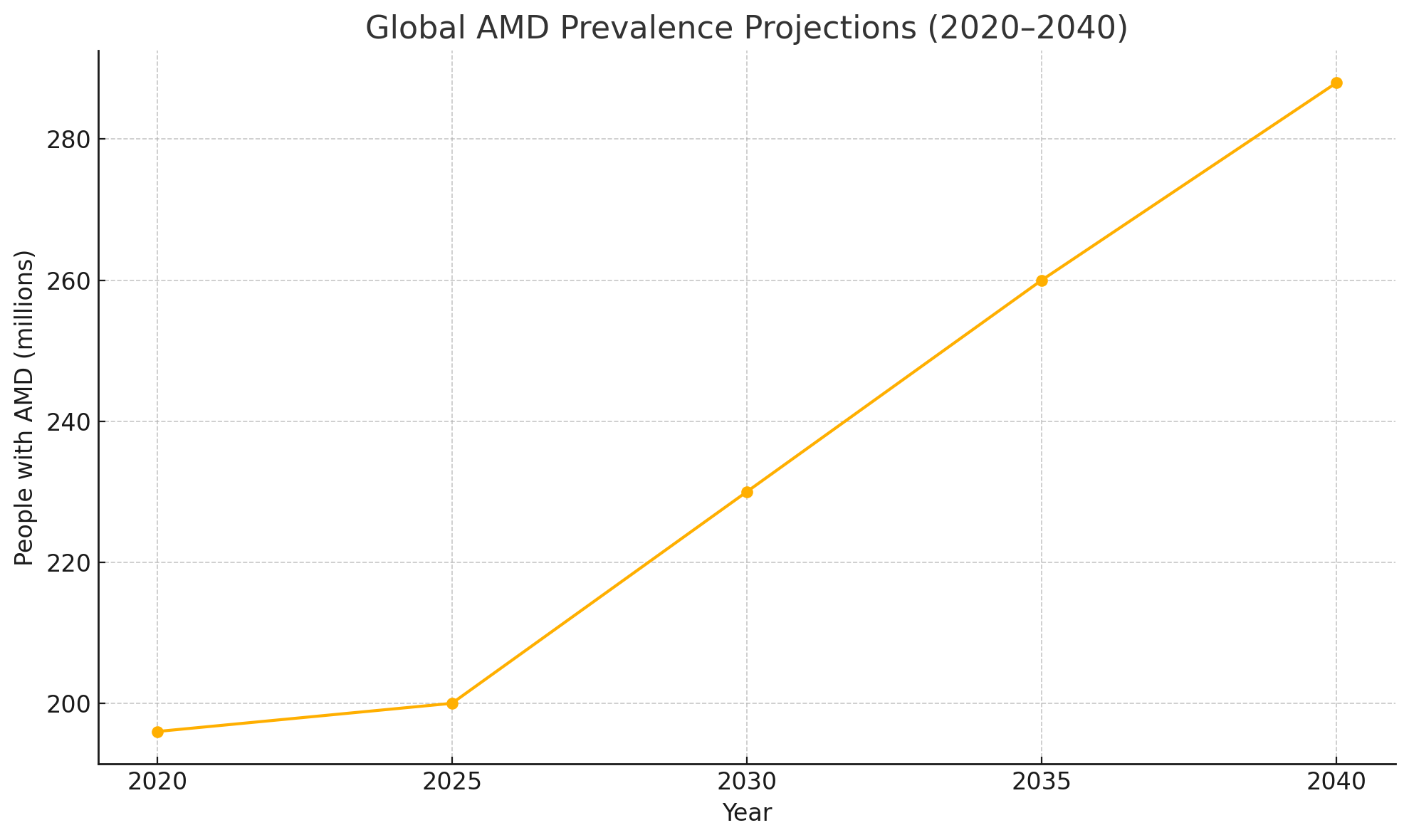
In 2026, roughly 200 million people worldwide are living with some form of AMD. That number is expected to rise a lot in the next coming decades because of the increase in global life expectancy and the increase of population aging, with projections estimating that we could hit 288 million cases by 2040.
AMD is responsible for approximately 8.7% of global blindness, making it one of the top leading causes of irreversible vision loss. In high-income regions such as North America, Europe and Australia, it remains the single largest cause of blindness in people over 60!
In the United States alone, roughly 20 million adults aged 40 and over have AMD, which can be roughly translated to about 12.6% of the population in this age bracket. Of these, approximately 1.49 million Americans have late-stage, vision-threatening AMD.
Globally, the burden of AMD is particularly concentrated in older adults:
• Ages 50–59: risk of advanced AMD is approximately 2%
• Ages 60–74: prevalence increases strongly
• Ages 75+: risk climbs to as high as 30%!
Age and Stage Distribution
AMD typically progresses through two main stages:
• Early/Intermediate AMD: Often asymptomatic but can lead to vision loss over time.
• Late-stage AMD: Neovascular (wet) AMD and Geographic atrophy (GA): which is responsible for the majority of severe vision loss.
In 2022, data from Asia estimated a crude prevalence of wet AMD at 42.7 per 1,000 people (around 4.3%). The age-standardised prevalence of wet AMD has more than doubled in the past decade from 10.7 per 1,000 in 2013 to 22.5 in 2022.
A U.S. study on Medicare Advantage members in 2025 showed a GA prevalence of 0.48% to 0.56%, which proves just how important, from a health and economical standpoint early detection is.
Regional Breakdown
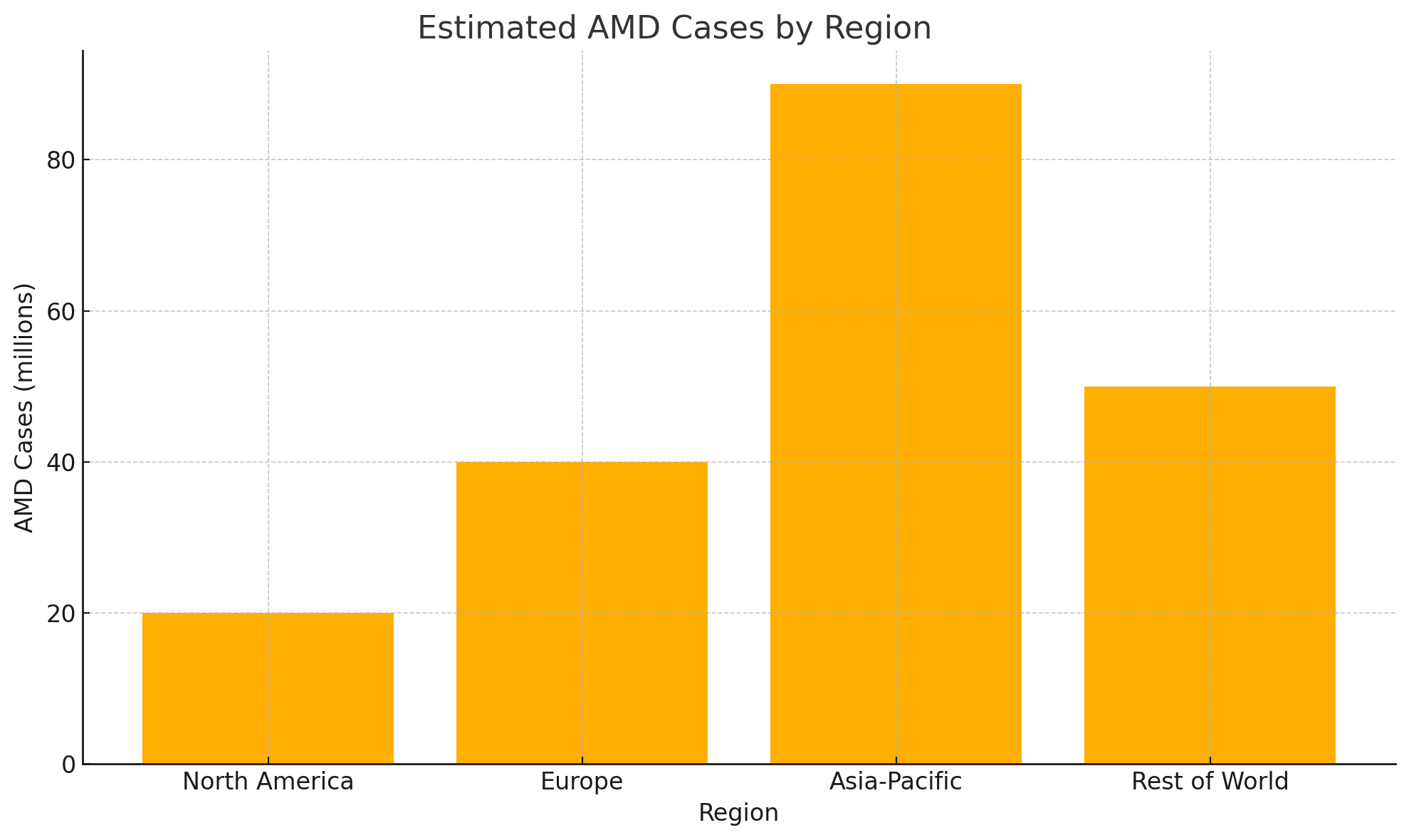
North America
• Roughly 20 million Americans aged 40+ are affected by AMD.
• 1.49 million have late-stage AMD.
• Wet AMD prevalence continues to rise in older adults.
• The U.S. market represents the largest share of global treatment revenue for AMD, because of its access to treatment services.
Europe and Oceania
• A very similar rate to North America.
• AMD is the leading cause of legal blindness in older adults in many countries, including the UK, Australia and Germany.
• Access to therapy is good but varies a lot depending on the country.
Asia
• Ageing populations at a very rapid scale in China, Japan, South Korea, and India are driving a massive surge in AMD cases.
• Asia is the fastest-growing AMD treatment market, driven by investment into eye care services.
Rest of the World
• Reliable AMD data is almost non-existent in Africa and parts of Latin America.
• Due to fewer routine eye exams and limited access to technology, AMD usually isn’t detected well enough in these regions.
Risk Factors
Key risk factors for AMD remain consistent:
• Age: By far the strongest predictor and the rate of disease rises significantly after age 60.
• Genetics.
• Smoking: A leading risk factor. Studies show it doubles the risk.
• Diet and cardiovascular health: Poor nutrition and vascular disease are a big contribution to the rise in AMD cases.
• Gender: Some studies show a higher wet AMD prevalence in men while others show higher GA rates in women.
Treatment Market Overview
• The Global AMD treatment market in 2025 was valued at a whopping $10.7 billion, up from $9.96 billion in 2024.
• This number should grow annually at around 7.5–7.7%, reaching over USD 14 billion by 2029.
• North America dominates the market with a nearly 48% share.
• Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region.
Economic and Public Health Impact
AMD’s impact on public health systems and economies is large:
• Costs are driven by treatment (e.g. $2,000–$2,600 per injection), vision rehabilitation and loss of independence.
• AMD contributes significantly to the estimated $411 billion global productivity loss from vision impairment.
• The burden of AMD will grow as we all live longer which makes it a key focus of ageing-related health policy.
Innovations and Future Directions
Several developments in the AMD space are shaping the future:
• Trials around Gene therapy
• AI-powered imaging tools
• Pharmaceutical investment. Merck’s acquisition of EyeBio for ~$3 billion in 2025 was an eye watering sum.
Conclusion
Macular degeneration is a massive cause of irreversible vision loss and it affects millions of older adults around the world. In 2026 with over 200 million cases and an ever ageing population that is growing fast, AMD is a clinical and a public health priority. Although treatments have improved dramatically in the last two decades, challenges remain around early detection, affordability and access especially in the lower and middle income regions.
The next five years will be critical. Gene therapy, AI imaging and pharmaceutical innovation could help in the fight against AMD, making care more effective and more accessible if the investment carries on being funnelled through.
Sources:
https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye...
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/langlo/article/...
https://www.brightfocus.org/macular/facts-figures/
https://www.fiercebiotech.com/biotech/merck-co-see...
https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/PressReleases/ag...
https://www.bayer.com/media/en-us/eylea-8-mg-appro...
https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles...

